对我们科研人员来说,细胞是实验中必不可少的部分,根据自身实验需要,我们需要从各种样本中制备单细胞悬液,例如血液中的细胞;源于组织样本中的细胞;源于贴壁细胞,比如单核诱导贴壁后形成的巨噬细胞、树突状细胞等;源于悬浮细胞等。针对不同的样本类型,如何制备高质量的单细胞悬液是我们大家比较关注的问题,今天给大家详细的介绍一下从多种样本中制备单细胞悬液的方法,希望对大家有用。
一、外周血样本
(图片来源网络)
人外周血单个核细胞(Peripheralblood mononuclear cells ,PBMCs )的分离制备:
1)医院及其血液中心采取的新鲜的肝素抗凝的2ml外周静脉血备用;
2)将肝素抗凝的静脉血用等体积的PBS稀释并充分混匀;
3)将人淋巴细胞分离液ficoll从 4 °C 取出,恢复至室温,取4ml转移至15ml 试管中备用;
4)用无菌吸管吸取稀释后的静脉血,沿管壁缓慢入至人淋巴细胞分离液液面上
(ficoll分离液:抗凝血1:1),缓缓地不要晃荡,保持界面的清楚;
5)将加完外周静脉血后的 50 ml 试管放入台式离心机中,2200 rpm 水平离心,
室温 25 min,注意离心机升降速都调至最慢,降速设置中一定要设置成no break,或者只有1成的制动。
6)离心完毕后,小心取出15 ml 试管,离心后管内可分为三层,在上、中层界面处有一层以单个核细胞为主的白色云雾层狭窄带,即为我们所需要的单个核细胞;
7)用无菌吸管吸取白色云雾层狭窄带的单个核细胞,并置于另一 15 ml 离心管
中,加入5mlPBS,1500 rpm,室温离心 5min,并充分洗涤细胞两次;
8)末次离心后,弃去上清,加入完全 RPMI 1640 培养液重悬细胞,充分混匀;
9)用白细胞计数液计数单个核细胞,根据实验所需,加入完全 1640培养液调整细胞浓度到所需要的浓度。

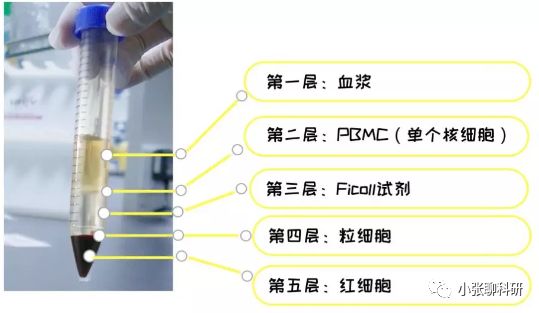
二、组织样本
(图片来源网络)
常见的组织类型:小鼠脾脏、肝脏、心脏、肺脏、脑组织、肿瘤组织、人肿瘤组织、皮肤组织……
传统组织处理方法:
机械法:网搓法、研磨法
适用样本类型:脾脏、淋巴结、胸腺
网搓法
1、将300 目尼龙网扎在无菌的小烧杯上;
2、把剪碎的组织放在网上,以眼科镊子轻轻搓组织块,边搓边加生理盐水冲洗,直到将组织搓完;
3、收集细胞悬液于离心管中, 1500rpm离心5min;
4、弃上清液,加红细胞裂解液重悬沉淀,室温作用5min,加等体积的PBS中和后,1500rpm离心5min,弃上清,用PBS洗涤一次,再用PBS重悬,细胞计数后即可使用。
研磨法
1、先将组织剪成1-2mm大小组织块;
2、放入组织研磨器中,转动研棒,研至匀浆;
3、加入10ml生理盐水,冲洗研磨器;
4、收获细胞悬液,并经200目尼龙网过滤,1500rpm离心5min;
5、弃上清液,加红细胞裂解液重悬沉淀,室温作用5min,加等体积的PBS中和后,1500rpm离心5min,弃上清,用PBS洗涤一次,再用PBS重悬,细胞计数后即可使用。
酶解法:胰蛋白酶类、胶原酶、溶菌酶、弹性蛋白酶
适用样本类型:肝脏、肾脏、心脏、肺脏、脊髓、脑、肠道、皮肤、肿瘤等;
操作步骤:
1、先将组织剪成泥状。
2 、用胰蛋白酶或胶原酶消化组织块,胰蛋白酶适用千消化细胞间质较少的软组织,如胚胎、上皮、肝、肾等组织。胰蛋白酌工作浓度一般为 0. 1 %—0 . 5 % 。对于纤维较多的组织或较硬的癌组织常用0 . 25 %胶原酶,胶原酌对组织中胶原蛋白类结构消化作用强,它仅对细胞间质有消化作用而对上皮细胞影响不大。胶原酶常用浓度为 0 . 1—0 . 3ug / ml ,用大于组织量30—50 倍的胰蛋白酶液或胶原酶液在 37°C ,摇床上消化组织,消化时间的长短依组织类型而定,一般来说,胰蛋白酶油作用 20—60 min,胶原酶需1—4h左右,一般还会加入DNA核酸内切酶。
3、消化完毕后,将细胞悬液通过200目孔径尼龙网过滤,以除掉未充分消化的组织;
4、已过滤的细胞悬液经1500rpm离心5min后,弃上清液,加红细胞裂解液重悬沉淀,室温作用5min,加等体积的PBS中和后,1500rpm离心5min,弃上清,用PBS洗涤一次,再用PBS重悬,细胞计数后即可使用。
下表整理了人和小鼠常见的不同组织处理方法,并附上参考文献,此内容来源于Worthington:
| Species |
Cells |
Enzyme(s) |
Reference |
| Human | 脂肪细胞 | 2型胶原酶:0.01-0.5% | Effect of Collagenase Concentration on The Isolation of Small Adipocytes from Human Buccal Fat Pad., J Oral Sci , 2018 |
| Human | 脂肪细胞 | Collagenase Type 1: 0.1% | Epigenome-wide Association Study of Body Mass Index, and the Adverse Outcomes of Adiposity, Nature541, 81, 2017 |
| Human | 基质细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.075% | Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction Provides a Source for Functional Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells., Cytotherapy 19, 1491-1500, 2017 |
| Human | 骨髓基质细胞
|
胶原酶1型:0.075% | Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Protect Human Cardiomyocytes from Amyloid Fibril Damage, Cytotherapy 19, 1426-1437, 2017 |
| Human | 间充质干细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.2% | Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alters Their Immunomodulatory Properties in a Tissue-Specific Manner., Stem Cells 35, 1636-1646, 2017 |
|
Human |
脂肪源内皮细胞 |
胶原酶1型:0.1% |
Autologous Cell Sources in Therapeutic Vasculogenesis: In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells from Peripheral Blood and Endothelial Cells Isolated from Adipose Tissue., Cytotherapy 18, 242-52, 2016 |
| Human | 脂肪干细胞 | 胶原酶1型:0.1% | High Glucose-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Generation Promotes Stemness in Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells,Cytotherapy 18, 371-83, 2016 |
|
Human |
骨髓基质细胞
|
胶原酶4型:0.2% |
Effect of Mild Heat Stress on the Proliferative and Differentiative Ability of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells., Cytotherapy17, 359-68, 2015 |
| Human | 脂肪干细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.1% | Expression Analysis of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells During In Vitro Differentiation to an Adipocyte Lineage., BMC Med Genomics 8, 41, 2015 |
|
Human |
脂肪基质
|
胶原酶1型:0.075% | Therapeutic Potential of Adipose-Derived SSEA-3-Positive Muse Cells for Treating Diabetic Skin Ulcers.,Stem Cells Transl Med 4, 146, 2015 |
| Human | 脂肪组织细胞
|
胶原酶1型:0.1% | Differential Effects of Processing Time and Duration of Collagenase Digestion on Human and Murine Fat Grafts.,Plast Reconstr Surg 136, 189e-199e, 2015 |
| Human | 脂肪基质血管细胞 | 中性蛋白酶:2.4 u/ml
胶原酶:250 u /毫升 |
Human White and Brite Adipogenesis is Supported by MSCA1 and is impaired by Immune Cells., Stem Cells 33, 1277-91, 2015 |
| Human |
脂肪源性间充质干细胞 |
胶原酶2型:0.1% | Defined Serum-Free Media for In Vitro Expansion of Adipose-DerivedMesenchymal Stem Cells., Cytotherapy 16, 915, 2014 |
| Human |
脂肪提取干细胞 |
胶原酶1型:0.15% |
Choosing the Right Type of Serum for Different Applications of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Influence on Proliferation and Differentiation Abilities.,Cytotherapy 16, 789, 2014 |
| Human | 间充质基质 | 胶原酶1型:0.1% | Proliferative and Phenotypical Characteristics of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Comparison of Ficoll Gradient Centrifugation and Red Blood Cell Lysis Buffer Treatment Purification Methods., Cytotherapy 16, 1220-8, 2014 |
|
Human |
脂肪间质干细胞 | 动物游离胶原酶:200u /ml | Xenofree Enzymatic Products for the Isolation of Human Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells., Tiss Eng 19, 473-8, 2013 |
| Human | 基质血管成分 | 胶原酶1型:0.075% | Stromal Vascular Fraction Isolated from Lipo-Aspirates Using an Automated Processing System: Bench and Bed Analysis., J Tissue Eng Regen Med 7, 864, 2013 |
|
Human |
脂肪干细胞 | 胶原酶1型:0.1% |
Platelet-Rich Plasma Greatly Potentiates Insulin-Induced Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Through a Serine/Threonine Kinase Akt-dependent Mechanism and Promotes Clinical Fat Graft Maintenance., Stem Cells Transl Med 1, 206-20, 2012 |
| Human | 血管周围干细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.1% | An Abundant Perivascular Source of Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering., Stem Cells Transl Med 1, 673, 2012 |
|
Human |
脂肪来源的间质血管 | 胶原酶1型:0.1% | Concise Review: Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma: Basic and Clinical Implications for TissueEngineering Therapies in Regenerative Surgery., Stem Cells Transl Med 1, 230-6, 2012 |
| Mouse | 脂肪基质 | 胶原酶1型:0.1% | Adipose Stromal Vascular Fraction-Mediated Improvements at Late-Stage Disease in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis., Stem Cells 35, 532-544, 2017 |
| Mouse | 脂肪间质细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.2% |
Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Minimize and Repair Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis.,Cytotherapy 18, 1129-45, 2016 |
| Mouse | 脂肪基质 | 胶原酶1型:0.1% | Improved Mobilization of Exogenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Bone for Fracture Healing and Sex Difference., Stem Cells 34, 2587-2600, 2016 |
|
Mouse |
脂肪细胞 | 胶原酶:0.1% | The Effects of A Single Developmentally-Entrained Pulse of Testosterone in Female Neonatal Mice On Reproductive and Metabolic Functions in Adult Life., Endocrinology 156, 3737, 2015 |
| Mouse | 间质血管细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.2% | Natural Killer T Cells in Adipose Tissue are Activated in Lean Mice., Exp Anim 62, 319, 2013 |
|
Mouse |
脂肪干细胞 | 胶原酶2型:0.1% | Biological and Clinical Availability of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Pelvic Dead Space Repair., Stem Cells Transl Med 1, 803, 2012 |
三、贴壁细胞
(图片来源网络)
贴壁细胞(adherent cells):活体体内细胞当离体置于体外培养时大多数以贴壁方式生长,主要包括正常细胞(例如:成纤维细胞、巨噬细胞、神经胶质细胞、心肌细胞以及肝、肺、肾、乳腺、皮肤细胞等)和肿瘤细胞。
胰蛋白酶消化
胰蛋白酶:最常用,浓度一般0.25%-5%,37℃消化时间一般1-5min,用血清终止;
四、脱落细胞
(图片来源网络)
临床上常见的脱落细胞经过简单处理就能制备成单细胞悬液,用于后续实验,具体操作:
1、食管拉网细胞的单细胞悬液的制备:
(1)将食管拉网器上的细胞洗脱到10ml PBS液中, 1500rpm,5min离心后,再用PBS液洗2次,800rpm,离心2min,弃上清;
(2)再加入PBS液5ml,以300目尼龙滤网过滤,离心沉淀去上清;
(3)加少许PBS液混匀沉淀细胞,备用。
2、胸、腹水脱落细胞的制备
(1)抽取胸、腹水50ml,加入1000U/ml肝素液1ml,放盐水瓶中置于4℃冰箱中静置6~12h,弃去上清;
(2)将底部10~20ml用长吸管移入试管中,用PBS液洗3次,以1500r/min离心沉淀5min;
(3)再加5ml PBS液混匀,用300目尼龙滤网过滤,离心沉淀去上清;
(4)加少许PBS液,混匀;加固定液或低温保存,备用。
3、冲洗液细胞样品的制备
(1)用300~500ml生理盐水冲洗膀胱,冲洗一定时间后,吸出冲洗液放入容器中于冰箱内置6~12h;
(2)取沉淀液20~40ml,离心沉淀并以生理盐水洗2次,吸上清;
(3)加10ml PBS液,混匀,以300目尼龙滤网过滤,离心沉淀去上清;
(4)过滤后1000rpm/min,10min,离心沉淀,去上清;加固定液或低温保存备用。